Investing in stocks can feel like navigating a maze, but understanding a stock’s true value doesn’t have to be complicated. By breaking it down into five simple steps, you can gain clarity on whether a stock is worth your investment. This guide uses plain English to explain how to evaluate a stock’s fundamentals, with real-world examples focusing on a well-known company, Apple Inc. (AAPL). Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned investor, these steps will help you make informed decisions.
1. Check the Company’s Financial Health
Before investing, think of a company like a person’s bank account. Is it earning more than it spends? Does it have too much debt? A company’s financial health gives you a snapshot of its stability.
Things to look for:-
- Look at Revenue and Profit: Revenue is the money a company makes, while profit is what’s left after expenses. Growing revenue and consistent profits are good signs.
- Check Debt Levels: Too much debt can be a red flag. Compare the company’s debt to its equity (assets minus liabilities) using the debt-to-equity ratio.
- Examine Cash Flow: Cash flow shows how much actual cash the company generates. Strong cash flow means it can pay bills and invest in growth.
Example for Apple: In 2024, Apple reported $394 billion in revenue and $99 billion in net income, showing strong profitability. Its debt-to-equity ratio is around 1.8, manageable for a company of its size. Apple’s free cash flow was $110 billion, reflecting its ability to fund innovation and return money to shareholders.
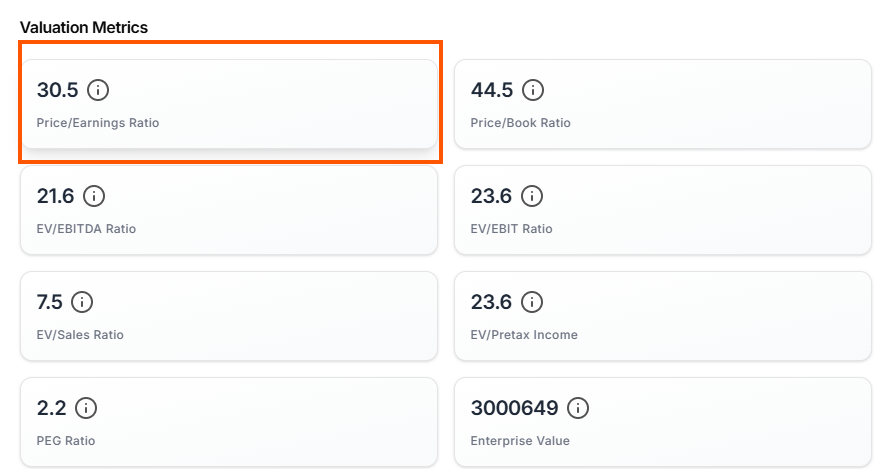
2. Understand the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
The P/E ratio is like a price tag for a stock. It tells you how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of the company’s earnings. A lower P/E might mean the stock is undervalued, while a high P/E could suggest it’s overpriced.
Things to look for:-
- Compare with Industry Peers: A P/E ratio only makes sense when compared to similar companies. For tech stocks, a P/E of 20-30 is common.
- Look at Historical P/E: Check the company’s P/E over time to see if the stock is cheaper or more expensive than usual.
- Consider Growth: A high P/E might be justified if the company is growing fast.
Example for Apple: Apple’s P/E ratio in early 2025 is around 28, slightly above the tech industry average of 25. Historically, Apple’s P/E has ranged from 15 to 40, so it’s not at its cheapest but reflects investor confidence in its growth, like new AI-driven products.
3. Analyze the Company’s Competitive Advantage
A company’s “moat” is what makes it stand out from competitors. A strong moat means the company can maintain profits over time, making its stock more valuable.
Things to look for:-
- Brand Strength: A strong brand can command loyal customers and higher prices.
- Unique Products or Technology: Patents, proprietary tech, or exclusive products create barriers for competitors.
- Market Share: Companies dominating their industry are often safer bets.
Example for Apple: Apple’s competitive advantage lies in its ecosystem (iPhone, Mac, App Store), which keeps customers loyal. Its brand is one of the most valuable globally, and its lead in smartphone and wearable markets (like Apple Watch) strengthens its moat.

4. Review News and Industry Trends
Stocks don’t exist in a vacuum. News and industry trends can impact a company’s future value. Staying informed helps you spot risks and opportunities.
Things to look for:-
- Monitor Company News: Look for product launches, lawsuits, or leadership changes that could affect the stock.
- Understand Industry Trends: Is the industry growing or shrinking? Are there new technologies disrupting it?
- Check Macro Factors: Economic conditions, like interest rates or inflation, can influence stock prices.
Example for Apple: In 2024, Apple announced AI-powered features for its iPhones, boosting investor optimism. However, regulatory scrutiny over App Store policies poses a risk. The tech industry is growing, but competition from companies like Samsung and Google remains fierce.
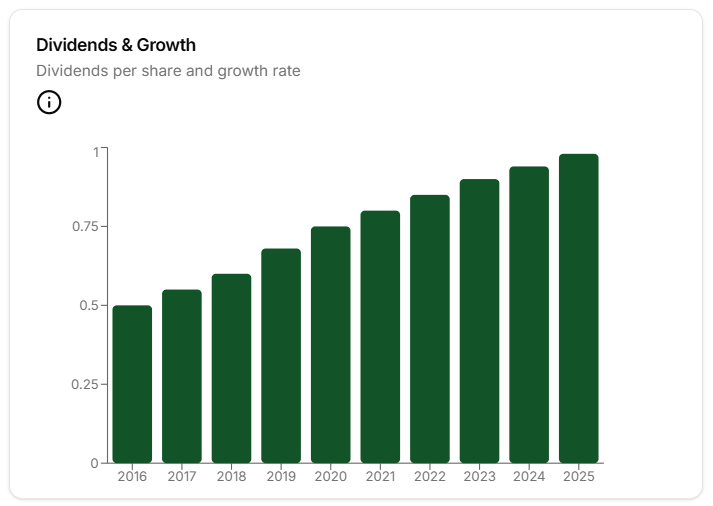
5. Evaluate Dividend and Buyback Programs
Companies that return money to shareholders through dividends or stock buybacks often signal confidence in their future. These programs can add value to your investment.
Subpoints:
- Dividend Yield: This shows how much a company pays out relative to its stock price. A steady or growing dividend is a positive sign.
- Stock Buybacks: When a company buys back its shares, it reduces the number of shares available, potentially increasing the stock’s value.
- Sustainability: Ensure the company can afford these programs without cutting into growth investments.
Example for Apple: Apple pays a dividend yield of about 0.5%, modest but reliable. In 2024, it spent $90 billion on share buybacks, reducing its share count and boosting earnings per share. This reflects Apple’s strong cash position and belief in its long-term value.
Conclusion
Understanding a stock’s true value is about looking beyond the stock price. By checking financial health, analyzing the P/E ratio, evaluating competitive advantages, staying updated on news, and reviewing shareholder programs, you can make smarter investment choices. Using Apple as an example, we see how a company’s strong fundamentals and market position make it a compelling stock to consider. Start applying these five steps today to build confidence in your investing journey.