Why Dividend Investing Belongs in Your Financial Toolkit

Dividend investing is a smart way to grow your money. It’s like getting rent payments, but instead of owning a house, you own part of a company. This payment is called a dividend.
Why Are Dividends Attractive?
Dividends offer both growth and stability, making them great for new investors. They give you regular income, which helps you reach your financial goals faster.
You can use this income to pay for things or buy more shares.
Dividends also help during rough market times. When stock prices drop, dividends can reduce some losses. This is helpful for new investors learning to handle market ups and downs.
Reinvesting Dividends
One big benefit of dividends is that you can reinvest them. This means buying more shares with the money you get. Over time, this makes your investment grow faster.
When you reinvest, you get more shares, and they earn more dividends. This cycle helps you build wealth over time. This is called compounding.
Dividend growth has been key to stock market returns. In the last 20 years, dividends per share went up by 5.6% each year. Experts think this will rise to about 7.6% a year. Since 1987, reinvested dividends have made up about 55% of market returns. More details are available from J.P. Morgan Asset Management.
How Experts Use Dividends
Professional investors use dividends in their plans. They like the steady income and growth potential.
You don’t need a lot of money to start. With careful planning, you can build a dividend portfolio that fits your goals. Dividend investing is a simple and effective way to grow wealth over time.
Taking Your First Steps: Building a Dividend Portfolio

Starting to invest in dividends might seem overwhelming. This part breaks it down into simple steps to help you begin.
Opening a Brokerage Account
The first thing to do is open a brokerage account. It’s like a bank account for your investments. Many sites, such as Fidelity, offer options that are easy for beginners to use and don’t cost much.
When picking a brokerage site, think about these points:
Fees: Lower fees mean you keep more money.
Minimum Investment: Some sites need a minimum amount to start. Pick one that fits your budget.
User-Friendliness: A simple and easy-to-use site is important, especially when you’re new.
Here’s a table to help you check out some popular choices:
Comparing Brokerage Accounts for Dividend Investors
This table looks at features of popular brokerage sites ideal for new dividend investors. It gives a quick look to help you decide.
|
Brokerage Platform |
Commission Fees |
Minimum Investment |
Dividend Reinvestment Plan |
Research Tools |
Mobile App Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fidelity |
$0 |
$0 |
Yes |
Yes |
4.5 stars |
|
Schwab |
$0 |
$0 |
Yes |
Yes |
4.0 stars |
|
Vanguard |
$0 |
$0 |
Yes |
Yes |
4.2 stars |
|
TD Ameritrade |
$0 |
$0 |
Yes |
Yes |
4.3 stars |
|
E*TRADE |
$0 |
$0 |
Yes |
Yes |
3.9 stars |
Note: This table is for illustrative purposes and actual offerings may vary. Please consult the respective brokerage websites for the most up-to-date information.
Many brokerages now let you trade without fees and don’t need a minimum amount to start. Check out the research tools and app ratings to find the one that fits you best.
How Much Money Do You Need?
You don’t need a lot of money to begin. Small, regular investments can grow over time due to compounding. Many platforms let you start with a little money.
Investing $50 each week, or an amount you feel comfortable with, is a good way to begin.
Choosing the Right Account Type
Different accounts offer tax benefits. Roth IRAs and Traditional IRAs can help with long-term goals like saving for retirement.
For short-term goals, a regular brokerage account might be better.
Setting Realistic Goals
Having clear goals helps you stay focused. Your goals should match your financial situation and timeline.
Short-Term Goals: Saving for a car down payment.
Long-Term Goals: Planning for retirement.
Overcoming Analysis Paralysis
New investors often overthink and delay starting. Don’t let this stop you. Begin with a simple plan and improve it as you go.
Lump-Sum vs. Regular Contributions
You can invest a large sum all at once (lump-sum investing) or make smaller, recurring contributions (dollar-cost averaging). For beginners, dollar-cost averaging can be a good strategy to navigate market fluctuations.
By following these steps, you can begin building a solid foundation for long-term financial growth and security through dividend investing.
Finding Dividend Gems: Simple Ways to Spot Quality Stocks
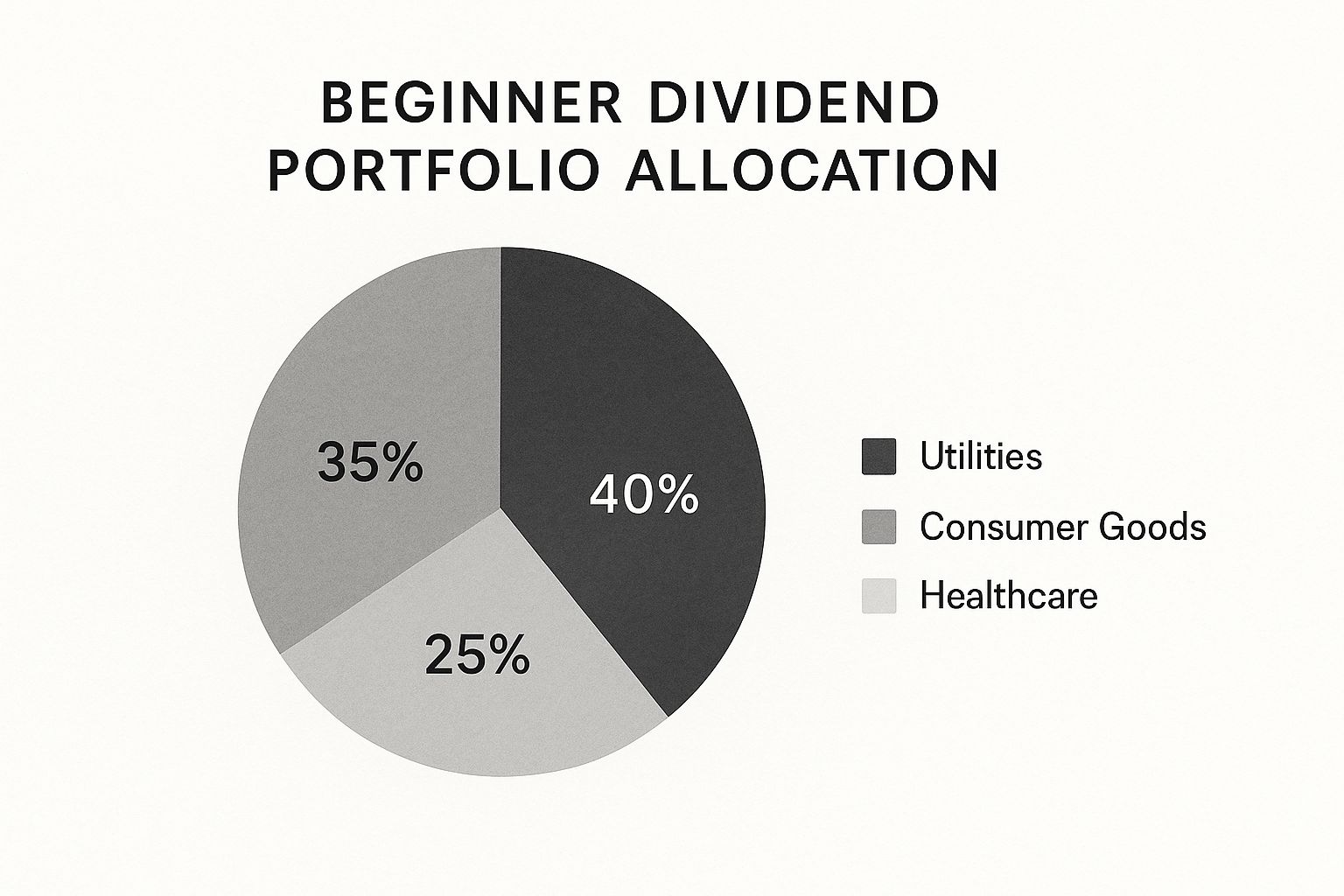
This pie chart shows how a new dividend investor might spread out their money. A lot is put into steady areas like Utilities and Consumer Goods, with less in Healthcare. This helps lower risk.
Choosing dividend stocks is like picking fresh fruit. You don’t just pick the biggest piece; you look for good quality. In dividend investing, it’s important to look beyond just a high dividend yield.
What to Look for in a Dividend Stock
Some key things can help you find good dividend stocks and make sure the company can keep paying over time.
Payout Ratio: This shows what part of a company’s earnings goes to dividends. A lower ratio, like 40%, means the company might raise payments later. A higher ratio, like 75%, could mean less room to grow, but it’s normal for big companies. More details on payout ratios are at Hartford Funds.
Dividend Growth: Growing dividends over time shows a company is doing well and wants to share profits.
Debt Levels: Lots of debt can make it hard for a company to keep paying dividends. Look for companies with less debt.
Earnings Stability: Steady earnings make dividends more reliable. Avoid companies with uneven earnings.
Dividend Aristocrats: The Best of Dividends
Dividend Aristocrats are companies that have raised their dividends for at least 25 years in a row. These companies are seen as top-notch in the dividend world, showing a strong focus on paying dividends. While past results don’t promise future ones, they do show a history of paying out.
Spotting Trouble: Warning Signs of a Dividend Cut
Sometimes, companies face challenges that force them to reduce or eliminate their dividends. Here are some warning signs to watch out for:
Falling Earnings: Declining earnings can signal financial distress and may indicate an inability to sustain current dividend levels.
Rising Debt: A significant increase in debt can put a strain on a company’s finances, potentially jeopardizing dividend payments.
Changes in Industry Conditions: Economic downturns or industry-specific disruptions can impact a company’s profitability and ability to maintain its dividend.
Putting It All Together
Using these metrics, you can start building a robust dividend portfolio. Begin by considering core sectors like Utilities, Consumer Goods, and Healthcare. The following table summarizes the essential metrics for beginners.
To help you get started, we’ve compiled a table summarizing the key metrics to consider.
Essential Dividend Stock Metrics for Beginners: A summary of the most important metrics to evaluate when selecting dividend stocks for a beginner portfolio
|
Metric |
What It Measures |
Ideal Range for Beginners |
Warning Signs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Payout Ratio |
Percentage of earnings paid as dividends |
30% – 70% |
Consistently Above 70% |
|
Dividend Growth Rate |
Annual percentage increase in dividends |
Positive and Consistent |
Declining or Negative Rate |
|
Debt-to-Equity Ratio |
Company’s debt compared to shareholder equity |
Below 1.0 |
Above 2.0 |
|
Earnings Stability |
Consistency and predictability of earnings |
Steady Growth or Stable Earnings |
Significant Fluctuations |
This table provides a quick reference for evaluating potential dividend stocks, helping you identify both promising opportunities and potential risks.
By understanding these simple principles, you can start building a dividend portfolio designed for steady income and long-term growth. It’s like planting a seed and nurturing it into a thriving tree.
Dividend ETFs: A Simple Way to Diversify
Choosing individual stocks can be hard for beginners. Dividend ETFs make it easy by bundling together companies that pay dividends. When you buy one, you own a piece of many businesses. This spreads out your risk, so if one company doesn’t do well, it won’t hurt your returns too much.
Choosing Between High-Yield and Dividend Growth ETFs
There are two main kinds of dividend ETFs: high-yield ETFs and dividend growth ETFs. High-yield ETFs focus on companies that pay big dividends now. Dividend growth ETFs look at companies that have been increasing their dividends over time.
High-yield ETFs might give you more money right away, but they might not grow much. Dividend growth ETFs often reinvest their earnings, which can help the company grow and increase dividends later.
Understanding Expense Ratios: The Fees
ETFs have charges called expense ratios. This is a small yearly fee to manage the fund. For example, a 0.10% fee means you pay $1 for every $1,000 you invest. It’s important to compare these fees when picking ETFs, as lower fees mean you keep more of your earnings. You can quickly find dividend stocks using a stock screener.
Looking at ETF Performance
Past performance doesn’t guarantee future results, but it can still be helpful. Check how an ETF has done in different market conditions, both good and bad. This can help you decide if it fits your investment goals. Global dividend payments have been strong. In 2024, they reached $1.73 trillion, up 4.2% from the year before. Although dividend yields are below average, the total paid out has grown a lot. Find out more about these trends here.
Choosing the Best ETF for You
Picking an ETF depends on your needs. Do you need money now, or are you saving for later? Do you prefer certain areas like healthcare or technology? Many online tools can help you find the ETF that matches your needs.
Success Story with Dividend ETFs
Jake, a regular investor, built a $1 million dividend portfolio using ETFs. He did this by picking the right ETFs and setting up automatic investments on the M1 platform. Jake focused on keeping things simple, reinvesting automatically, and thinking long-term. His story shows that dividend ETFs can help you reach financial goals, even if you don’t know much about the market. This makes dividend ETFs easy for beginners who want passive income and financial freedom.
Choosing a good dividend ETF can make investing easier. It’s like having experts pick stocks for you, giving you a mixed portfolio without the hassle of researching each company.
The Magic of Dividend Reinvestment: Grow Your Wealth
Dividend reinvestment is where investing in dividends really works well. It’s like a snowball rolling downhill, getting bigger and bigger. This helps build wealth over time.
What Are Dividend Reinvestment Plans (DRIPs)?
Dividend Reinvestment Plans, or DRIPs, let you reinvest your dividends to buy more shares automatically. Instead of getting cash, you get more shares of the same company or ETF. These new shares earn dividends too, creating ongoing growth. This is how compounding works.
Think of two investors, both starting with $1,000. One spends their dividends, the other reinvests them. Over time, the one who reinvests will see bigger returns thanks to compounding.
How to Set Up Automatic Reinvestment
Most brokerages make it easy to set up automatic dividend reinvestment. Here’s a simple guide:
Log in to your brokerage account.
Find the “Dividend Reinvestment” or “DRIP” section.
Choose the investments you want to enroll.
Confirm and save your choices.
The steps might change a bit depending on your brokerage. Check your brokerage’s help section for more details.
When to Take Cash Dividends
While reinvesting is often a good idea, sometimes taking cash is better:
Need Income: If you need dividends for expenses, getting cash is necessary.
Diversify: You might want to use cash to invest in other stocks or sectors.
Real-Life Success with Dividend Reinvestment
Many investors have reached financial independence through dividend reinvestment. Jake is one example. He built a $1 million dividend portfolio using ETFs and automatic reinvestment on the M1 platform. He credits simplicity and automatic reinvestment for his success. You can read more about his story on M1’s blog.
The Benefits of Dividend Reinvestment
For new investors, dividend reinvestment is an easy way to grow wealth. It keeps emotions out of investing by reinvesting dividends automatically, no matter what the market is doing. This can be helpful for those who find saving hard.
Dividend reinvestment is key to building wealth over time. By learning how it works and setting up automatic reinvestment, you can use compounding to reach your financial goals.
Avoiding The Costly Mistakes That Trip Up New Dividend Investors

Dividend investing offers a reliable path to building wealth. However, several common mistakes can hinder your progress. This section explores these pitfalls and provides guidance on how to avoid them.
The Lure Of High Yields: Too Good To Be True?
New investors are sometimes drawn to the allure of exceptionally high dividend yields. But a significantly high yield can be a red flag, potentially indicating that the company is struggling financially and the dividend isn’t sustainable. Instead of chasing high yields, prioritize finding stocks with healthy payout ratios and a history of consistent dividend growth. This approach can lead to more stable and reliable returns over time.
Putting All Your Eggs In One Basket: The Importance Of Diversification
Concentrating all your investments in a single company or industry sector exposes you to significant risk. If that company or sector experiences difficulties, your entire portfolio could suffer substantial losses. Diversification, spreading your investments across various companies and industries, is crucial for mitigating risk and building a more resilient portfolio. Dividend ETFs can be a valuable tool for achieving instant diversification.
Emotional Investing: Staying Calm During Market Downturns
Market ups and downs are normal. It’s normal to feel worried when prices drop. But making choices based on feelings, like selling in a panic, can hurt your returns over time. Keep your investment goals in mind and stick to your plan. A compound interest calculator shows how reinvesting dividends can help in the long run.
Overlooking Taxes: Qualified Vs. Non-Qualified Dividends
Qualified dividends have lower taxes compared to non-qualified dividends. This can affect your total return. Holding stocks for a certain time can make dividends eligible for lower taxes. Tax-beneficial accounts like Roth IRAs and Traditional IRAs can also help. Knowing these details can boost your after-tax returns.
Action Steps To Protect Your Portfolio:
Research Carefully: Don’t buy just because of high dividends. Check a company’s finances and business model first.
Diversify: Spread your money across different sectors and companies to reduce risk.
Think Long-Term: Don’t sell in panic during market drops. Stay focused on your long-term goals.
Understand Taxes: Know the difference between qualified and non-qualified dividends for better tax planning.
Be Patient: Building a strong dividend portfolio takes time and discipline. Stay steady and avoid quick decisions.
By avoiding these common errors, you can do well in dividend investing. Start small, stay updated, and let compounding work for you.
Want to improve your dividend investing and avoid common mistakes? Stock Decisions offers easy-to-understand insights to help you make wise choices. Visit today and invest with confidence.
